
Cette galerie contient 1 photo.
Mes preférés : lsof, strace, netstat, tcpdump, top.

Je viens de lire l’article : https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/new-stealthy-linux-malware-used-to-backdoor-systems-for-years/
Command-and-control servers historically used by the malware have domains registered six years ago, in December 2015, all of them
| FileName | MD5 | Detection | First Seen in VT |
|---|---|---|---|
| systemd-daemon | 1d45cd2c1283f927940c099b8fab593b | 0/61 | 2018-05-16 04:22:59 |
| systemd-daemon | 11ad1e9b74b144d564825d65d7fb37d6 | 0/58 | 2018-12-25 08:02:05 |
| systemd-daemon | 5c0f375e92f551e8f2321b141c15c48f | 0/56 | 2020-05-08 05:50:06 |
| gvfsd-helper | 64f6cfe44ba08b0babdd3904233c4857 | 0/61 | 2021-01-18 13:13:19 |
J’ai donc rapidement fait :
# sudo find / -name 'systemd-daemon' # sudo find / -name 'gvfsd-helper'
Aucun n’est présent …
Sous Mac OS j’avais fait plusieurs articles …Mais sous Ubuntu c’est plus simple, voici les commandes que j’utilise :
$ du -sh Images/
$ find Images/ -iname '*.jpg' -exec mogrify \{} -verbose -resize 1920x1080\> \{} \;
$
Je considère que la résolution max est 1920×1080 (on peut aussi prendre 2048×1536). Il est vivement conseillé d’avoir un backup avant de lancer les commandes. Et je vous conseille cette lecture : https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Impression_photo_num%C3%A9rique
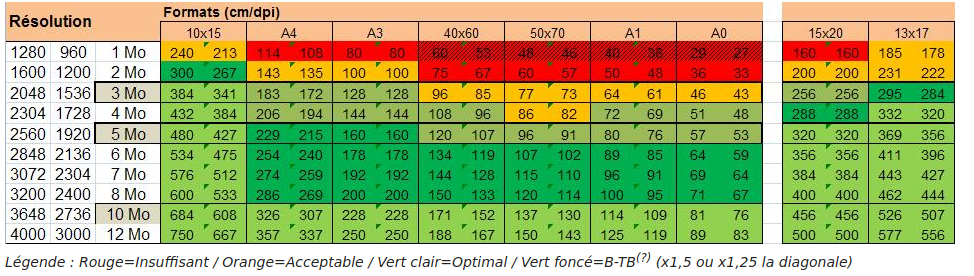 A noter aussi que je déplace toutes les vidéos avant de lancer la commandes :
A noter aussi que je déplace toutes les vidéos avant de lancer la commandes :
$ find Images/ -iname *.mp4 -exec mv "{}" ./Vidéos/. \;
$ find Images/ -iname *.mov -exec mv "{}" ./Vidéos/. \;
$ find Images/ -iname *.avi -exec mv "{}" ./Vidéos/. \;
$ find Images/ -iname *.mpg -exec mv "{}" ./Vidéos/. \;
$ find Images/ -iname *.3gp -exec mv "{}" ./Vidéos/. \;
$ find Images/ -iname *.3g2 -exec mv "{}" ./Vidéos/. \;
A noter aussi que je conseille vivement cette commande afin de voir si le répertoire contient que des images :
$ find Images/ -type f | sed -n 's/..*\.//p' | sort | uniq -c
36 bmp
5 db
10 gif
2 GIF
466 jpeg
61698 jpg
1 Jpg
47063 JPG
47 png
118 PNG
A noter aussi que pour classer mes vidéos, j’ai le même process que pour mes photos :
/Vidéos$ fdupes -rdN . /Vidéos$ time exiftool -v -r "-filemodifydate<datetimeoriginal" "-filecreateddate<datetimeoriginal" *.* /Vidéos$ sortphotos -r . . --sort %Y/%m/%d /Vidéos$
Maintenant je vais utiliser Digikam pour me faire une base de donnée d’images identique (mais avec une compression différente) … et utiliser sqllite3 pour exploiter cette base.
$ sudo apt-get install sqlite3 libsqlite3-dev $ sqlite3 similarity.db SQLite version 3.22.0 2018-01-22 18:45:57 Enter ".help" for usage hints. sqlite> .table ImageHaarMatrix ImageSimilarity SimilaritySettings sqlite> .quit
A suivre
My current issue on Oracle Linux 7.3 (kernel 4.1.12-61.1.18): I have only one processor or issue « Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) ». Impossible to boot without issue « Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) » and 8 processors.
To see the number of processor : cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep « model name »
My processor is : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2623 v3 @ 3.00GHz
All my test done :
| Tests | Status | Processor | Note | Grub parameter |
| 1 | OK | 1 | quiet splash noapic nolapic acpi=off | |
| 2 | OK | 1 | quiet acpi=off | |
| 3 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet | |
| 4 | KO | No boot | quiet splash pci=noacpi | |
| 5 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet acpi=off nr_cpus=8 | |
| 6 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet acpi=ht | |
| 7 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet acpi=noirq | |
| 8 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet pnpacpi=off | |
| 9 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet pcie_aspm=off | |
| 10 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet pci=noacpi | |
| 11 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet acpi=ht nolapic splash | |
| 12 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet acpi=ht pci=nocrs | |
| 13 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet acpi=ht acpi_osi=Linux | |
| 14 | OK | 1 | quiet idle=poll acpi=off | |
| 15 | OK | 1 | quiet idle=poll acpi=off processor.nocst=1 | |
| 16 | OK | 1 | quiet acpi=off processor.nocst=1 | |
| 17 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet acpi=ht acpi.nopower_check=1 acpi_osi=Linux | |
| 18 | OK | 1 | quiet acpi=off processor.nocst=1 maxcpus=8 | |
| 19 | OK | 1 | quiet intel_iommu=on acpi=off noapi | |
| 20 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet noapic pci=assign-busses apicmaintimer idle=poll reboot=cold,hard | |
| 21 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet pci=nomsi | |
| 22 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet pci=noaer | |
| 23 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet splash noapic nolapic acpi=ht pci=nocrs | |
| 24 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet splash noapic nolapic acpi=noirq pci=nocrs | |
| 25 | KO | Freeze : Unsupported PM cap regs version (7) | quiet splash nomodeset acpi_osi=Linux |
When I see the source code of pci.c :
/**
* pci_pm_init - Initialize PM functions of given PCI device
* @dev: PCI device to handle.
*/
void pci_pm_init(struct pci_dev *dev)
{
int pm;
u16 pmc;
pm_runtime_forbid(&dev->dev);
pm_runtime_set_active(&dev->dev);
pm_runtime_enable(&dev->dev);
device_enable_async_suspend(&dev->dev);
dev->wakeup_prepared = false;
dev->pm_cap = 0;
dev->pme_support = 0;
/* find PCI PM capability in list */
pm = pci_find_capability(dev, PCI_CAP_ID_PM);
if (!pm)
return;
/* Check device's ability to generate PME# */
pci_read_config_word(dev, pm + PCI_PM_PMC, &pmc);
if ((pmc & PCI_PM_CAP_VER_MASK) > 3) {
pci_err(dev, "unsupported PM cap regs version (%u)\n",
pmc & PCI_PM_CAP_VER_MASK);
return;
}
acpi= [HW,ACPI,X86,ARM64] Advanced Configuration and Power Interface Format: { force | on | off | strict | noirq | rsdt | copy_dsdt } force -- enable ACPI if default was off on -- enable ACPI but allow fallback to DT [arm64] off -- disable ACPI if default was on noirq -- do not use ACPI for IRQ routing strict -- Be less tolerant of platforms that are not strictly ACPI specification compliant. rsdt -- prefer RSDT over (default) XSDT copy_dsdt -- copy DSDT to memory For ARM64, ONLY "acpi=off", "acpi=on" or "acpi=force" are availablepnpacpi= [ACPI] { off }nr_cpus= [SMP] Maximum number of processors that an SMP kernel could support. nr_cpus=n : n >= 1 limits the kernel to support 'n' processors. It could be larger than the number of already plugged CPU during bootup, later in runtime you can physically add extra cpu until it reaches n. So during boot up some boot time memory for per-cpu variables need be pre-allocated for later physical cpu hot plugging.pcie_aspm= [PCIE] Forcibly enable or disable PCIe Active State Power Management. off Disable ASPM. force Enable ASPM even on devices that claim not to support it. WARNING: Forcing ASPM on may cause system lockups.pci=option[,option...] [PCI] various PCI subsystem options: earlydump [X86] dump PCI config space before the kernel changes anything off [X86] don't probe for the PCI bus bios [X86-32] force use of PCI BIOS, don't access the hardware directly. Use this if your machine has a non-standard PCI host bridge. nobios [X86-32] disallow use of PCI BIOS, only direct hardware access methods are allowed. Use this if you experience crashes upon bootup and you suspect they are caused by the BIOS. conf1 [X86] Force use of PCI Configuration Access Mechanism 1 (config address in IO port 0xCF8, data in IO port 0xCFC, both 32-bit). conf2 [X86] Force use of PCI Configuration Access Mechanism 2 (IO port 0xCF8 is an 8-bit port for the function, IO port 0xCFA, also 8-bit, sets bus number. The config space is then accessed through ports 0xC000-0xCFFF). See http://wiki.osdev.org/PCI for more info on the configuration access mechanisms. noaer [PCIE] If the PCIEAER kernel config parameter is enabled, this kernel boot option can be used to disable the use of PCIE advanced error reporting. nodomains [PCI] Disable support for multiple PCI root domains (aka PCI segments, in ACPI-speak). nommconf [X86] Disable use of MMCONFIG for PCI Configuration check_enable_amd_mmconf [X86] check for and enable properly configured MMIO access to PCI config space on AMD family 10h CPU nomsi [MSI] If the PCI_MSI kernel config parameter is enabled, this kernel boot option can be used to disable the use of MSI interrupts system-wide. noioapicquirk [APIC] Disable all boot interrupt quirks. Safety option to keep boot IRQs enabled. This should never be necessary. ioapicreroute [APIC] Enable rerouting of boot IRQs to the primary IO-APIC for bridges that cannot disable boot IRQs. This fixes a source of spurious IRQs when the system masks IRQs. noioapicreroute [APIC] Disable workaround that uses the boot IRQ equivalent of an IRQ that connects to a chipset where boot IRQs cannot be disabled. The opposite of ioapicreroute. biosirq [X86-32] Use PCI BIOS calls to get the interrupt routing table. These calls are known to be buggy on several machines and they hang the machine when used, but on other computers it's the only way to get the interrupt routing table. Try this option if the kernel is unable to allocate IRQs or discover secondary PCI buses on your motherboard. rom [X86] Assign address space to expansion ROMs. Use with caution as certain devices share address decoders between ROMs and other resources. norom [X86] Do not assign address space to expansion ROMs that do not already have BIOS assigned address ranges. nobar [X86] Do not assign address space to the BARs that weren't assigned by the BIOS. irqmask=0xMMMM [X86] Set a bit mask of IRQs allowed to be assigned automatically to PCI devices. You can make the kernel exclude IRQs of your ISA cards this way. pirqaddr=0xAAAAA [X86] Specify the physical address of the PIRQ table (normally generated by the BIOS) if it is outside the F0000h-100000h range. lastbus=N [X86] Scan all buses thru bus #N. Can be useful if the kernel is unable to find your secondary buses and you want to tell it explicitly which ones they are. assign-busses [X86] Always assign all PCI bus numbers ourselves, overriding whatever the firmware may have done. usepirqmask [X86] Honor the possible IRQ mask stored in the BIOS $PIR table. This is needed on some systems with broken BIOSes, notably some HP Pavilion N5400 and Omnibook XE3 notebooks. This will have no effect if ACPI IRQ routing is enabled. noacpi [X86] Do not use ACPI for IRQ routing or for PCI scanning. use_crs [X86] Use PCI host bridge window information from ACPI. On BIOSes from 2008 or later, this is enabled by default. If you need to use this, please report a bug. nocrs [X86] Ignore PCI host bridge windows from ACPI. If you need to use this, please report a bug. routeirq Do IRQ routing for all PCI devices. This is normally done in pci_enable_device(), so this option is a temporary workaround for broken drivers that don't call it. skip_isa_align [X86] do not align io start addr, so can handle more pci cards noearly [X86] Don't do any early type 1 scanning. This might help on some broken boards which machine check when some devices' config space is read. But various workarounds are disabled and some IOMMU drivers will not work. bfsort Sort PCI devices into breadth-first order. This sorting is done to get a device order compatible with older (<= 2.4) kernels. nobfsort Don't sort PCI devices into breadth-first order. pcie_bus_tune_off Disable PCIe MPS (Max Payload Size) tuning and use the BIOS-configured MPS defaults. pcie_bus_safe Set every device's MPS to the largest value supported by all devices below the root complex. pcie_bus_perf Set device MPS to the largest allowable MPS based on its parent bus. Also set MRRS (Max Read Request Size) to the largest supported value (no larger than the MPS that the device or bus can support) for best performance. pcie_bus_peer2peer Set every device's MPS to 128B, which every device is guaranteed to support. This configuration allows peer-to-peer DMA between any pair of devices, possibly at the cost of reduced performance. This also guarantees that hot-added devices will work. cbiosize=nn[KMG] The fixed amount of bus space which is reserved for the CardBus bridge's IO window. The default value is 256 bytes. cbmemsize=nn[KMG] The fixed amount of bus space which is reserved for the CardBus bridge's memory window. The default value is 64 megabytes. resource_alignment= Format: [<order of align>@][<domain>:]<bus>:<slot>.<func>[; ...] [<order of align>@]pci:<vendor>:<device>\ [:<subvendor>:<subdevice>][; ...] Specifies alignment and device to reassign aligned memory resources. If <order of align> is not specified, PAGE_SIZE is used as alignment. PCI-PCI bridge can be specified, if resource windows need to be expanded. To specify the alignment for several instances of a device, the PCI vendor, device, subvendor, and subdevice may be specified, e.g., 4096@pci:8086:9c22:103c:198f ecrc= Enable/disable PCIe ECRC (transaction layer end-to-end CRC checking). bios: Use BIOS/firmware settings. This is the the default. off: Turn ECRC off on: Turn ECRC on. hpiosize=nn[KMG] The fixed amount of bus space which is reserved for hotplug bridge's IO window. Default size is 256 bytes. hpmemsize=nn[KMG] The fixed amount of bus space which is reserved for hotplug bridge's memory window. Default size is 2 megabytes. hpbussize=nn The minimum amount of additional bus numbers reserved for buses below a hotplug bridge. Default is 1. realloc= Enable/disable reallocating PCI bridge resources if allocations done by BIOS are too small to accommodate resources required by all child devices. off: Turn realloc off on: Turn realloc on realloc same as realloc=on noari do not use PCIe ARI. pcie_scan_all Scan all possible PCIe devices. Otherwise we only look for one device below a PCIe downstream port.
Test 19 : Log exemple in /var/log/message :
Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-4.1.12-61.1.18.el7uek.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet intel_iommu=on acpi=off noapi LANG=en_GB.UTF-8
...
#011RCU restricting CPUs from NR_CPUS=8192 to nr_cpu_ids=1.
...
RCU: Adjusting geometry for rcu_fanout_leaf=16, nr_cpu_ids=1
...
CPU: Physical Processor ID: 0
CPU: Processor Core ID: 0
...
smpboot: SMP motherboard not detected
smpboot: SMP disabled
...
x86: Booted up 1 node, 1 CPUs
smpboot: Total of 1 processors activated (5993.31 BogoMIPS)
NMI watchdog: enabled on all CPUs, permanently consumes one hw-PMU counter.
Grep : grep « Kernel command line: » messages*
... Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-4.1.12-61.1.18.el7uek.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet noapic pci=assign-busses apicmaintimer idle=poll reboot=cold,hard LANG=en_GB.UTF-8 ... Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-3.10.0-514.el7.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet noapic pci=assign-busses apicmaintimer idle=poll reboot=cold,hard LANG=en_GB.UTF-8 ... ... Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-4.1.12-61.1.18.el7uek.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet noapic pci=assign-busses apicmaintimer idle=poll reboot=cold,hard LANG=en_GB.UTF-8 ... Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-4.1.12-61.1.18.el7uek.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet acpi=ht pci=nocrs LANG=en_GB.UTF-8 ... Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-4.1.12-61.1.18.el7uek.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet pci=nomsi LANG=en_GB.UTF-8 ... Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-4.1.12-61.1.18.el7uek.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet noapic pci=assign-busses apicmaintimer idle=poll reboot=cold,hard LANG=en_GB.UTF-8 ... Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-4.1.12-61.1.18.el7uek.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet splash noapic nolapic acpi=off LANG=en_GB.UTF-8 ... Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-4.1.12-61.1.18.el7uek.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet intel_iommu=on acpi=off noapi LANG=en_GB.UTF-8 ... Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-4.1.12-61.1.18.el7uek.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet intel_iommu=on acpi=off noapi LANG=en_GB.UTF-8 ...
More logs of issue on PCI :
Kernel command line: BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-4.1.12-61.1.18.el7uek.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/ol-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=ol/root rd.lvm.lv=ol/swap rhgb quiet splash noapic nolapic acpi=off LANG=en_GB.UTF-8
...
kernel: PCI: Probing PCI hardware
kernel: PCI host bridge to bus 0000:00
kernel: pci_bus 0000:00: root bus resource [io 0x0000-0xffff]
kernel: pci_bus 0000:00: root bus resource [mem 0x00000000-0x3fffffffffff]
kernel: pci_bus 0000:00: No busn resource found for root bus, will use [bus 00-ff]
kernel: pci 0000:00:01.0: PCI bridge to [bus 01]
kernel: pci 0000:00:03.0: PCI bridge to [bus 04]
kernel: pci 0000:05:00.0: disabling ASPM on pre-1.1 PCIe device. You can enable it with 'pcie_aspm=force'
kernel: pci 0000:00:03.2: PCI bridge to [bus 05-06]
kernel: pci 0000:06:04.0: unsupported PM cap regs version (7)
kernel: pci 0000:05:00.0: PCI bridge to [bus 06]
kernel: pci 0000:00:1c.0: PCI bridge to [bus 07]
kernel: pci 0000:00:1c.1: PCI bridge to [bus 08-0c]
kernel: pci 0000:08:00.0: PCI bridge to [bus 09-0c]
kernel: pci 0000:09:00.0: PCI bridge to [bus 0a-0b]
kernel: vgaarb: setting as boot device: PCI:0000:0b:00.0
kernel: vgaarb: device added: PCI:0000:0b:00.0,decodes=io+mem,owns=io+mem,locks=none
kernel: pci 0000:0a:00.0: PCI bridge to [bus 0b]
kernel: pci 0000:00:1c.2: PCI bridge to [bus 02]
kernel: pci 0000:00:1c.3: PCI bridge to [bus 03]
kernel: pci 0000:00:1f.0: default IRQ router [8086:8d44]